Publication in the journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
Optimisation of xylanases production by two Cellulomonas strains and their use for biomass deconstruction
We are proud to highlight the remarkable capabilities of our JFermi benchtop bioreactors in facilitating advanced enzyme production research. Recently, enzyme production of *Cellulomonas fimi* and *Cellulomonas* sp. B6 was conducted in our 500-mL benchtop bioreactors, demonstrating the versatility and precision of our equipment.
Experimental Setup
– Bioreactor Volume: 500 mL benchtop bioreactors filled with 300 mL of MM medium.
– Supplementation: MM medium supplemented with 1% w/w PWP and WB, respectively.
– Starter Cultures: Bacteria initially grown in LB medium and then inoculated into the MM medium to achieve an initial cell concentration corresponding to an OD of 0.05.
– Conditions: Enzyme production carried out in duplicates at 30 °C for 72 hours with daily sampling.
Bioreactor Features
Our bioreactors are equipped with advanced features to ensure optimal conditions for enzyme production:
– Dissolved Oxygen Control: The bioreactors can control the dissolved oxygen (DO) level by adjusting the agitation and air flow rate. For this experiment, the DO level was maintained at 20% of saturation to ensure aerobic conditions.
– pH Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the pH in the culture medium to maintain stability and optimal growth conditions.
– Temperature Control: Precise temperature regulation to maintain the required 30 °C throughout the production process.
These features enable researchers to conduct highly controlled and reproducible experiments, making our bioreactors an invaluable tool for enzyme production and other biotechnological applications. We are excited to see the innovative research being conducted with our bioreactors and look forward to supporting more scientific advancements in the future. Stay tuned for more updates on how JFermi’s bioreactors are making a difference in the world of biotechnology!
Abstract:
One of the main distinguishing features of bacteria belonging to the Cellulomonas genus is their ability to secrete multiple polysaccharide degrading enzymes. However, their application in biomass deconstruction still constitutes a challenge. We addressed the optimisation of the xylanolytic activities in extracellular enzymatic extracts of Cellulomonas sp. B6 and Cellulomonas fimi B-402 for their subsequent application in lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis by culture in several substrates. As demonstrated by secretomic profiling, wheat bran and waste paper resulted to be suitable inducers for the secretion of xylanases of Cellulomonas sp. B6 and C. fimi B-402, respectively. Both strains showed high xylanolytic activity in culture supernatant although Cellulomonas sp. B6 was the most efficient xylanolytic strain. Upscaling from flasks to fermentation in a bench scale bioreactor resulted in equivalent production of extracellular xylanolytic enzymatic extracts and freeze drying was a successful method for concentration and conservation of the extracellular enzymes, retaining 80% activity. Moreover, enzymatic cocktails composed of combined extra and intracellular extracts effectively hydrolysed the hemicellulose fraction of extruded barley straw into xylose and xylooligosaccharides.
Enzyme production in bench-top bioreactor
Enzyme production of C. fimi and Cellulomonas sp. B6 was performed in 500-mL bench-top bioreactors (JFermi Ltd., Jenő, Hungary) filled with 300 mL of MM medium supplemented with 1% w/w PWP and WB, respectively. Bacteria were first grown as starter cultures in LB medium and then inoculated into the MM supplemented with biomass to get an initial cell concentration that corresponds to an OD of 0.05. Enzyme productions, in duplicates, were accomplished at 30 °C for 72 h with daily sampling. The bioreactors were equipped to be able to control dissolved oxygen (DO) level by adjusting the agitation and air flow rate, and to monitor the pH in the culture medium. DO level was kept at 20% of saturation in order to ensure that the culture was maintained in aerobic conditions.
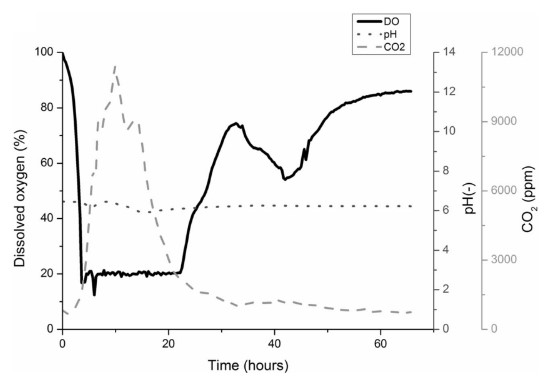
Profile of Cellulomonas sp. B6 cultures on wheat bran (WB) in bench-top bioreactor (3L). Temperature and pH were maintained at 30 °C and 7, respectively
Source:
AMB 2021 Optimisation of xylanases production by Cellulomonas,
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00253-021-11305-y
